Projet Glyco@Alps2 : Study and valorisation of carbohydrates
Les partenaires du projet
IBS, LGP2, CERMAV, DCM, DPM, GIN, IAB, LPCV, LRP, 3SR, SAJV, GAEL, MEM, SYMMES, G-SCOP, LECA, EMR-BRM, AECC/ENSAG, CEA-LETI, CEA-LITEN, ILL, ESRF
Contexte et Objectifs du projet
Après 4 ans de projet transversal, le programme Glyco@Alps2 continuera à explorer la diversité et la complexité structurelle des sucres, y compris ceux que l'on trouve dans la biodiversité alpine, et se concentre sur leur exploitation pour les produits biopharmaceutiques, les diagnostics médicaux, la médecine personnalisée, les matériaux et les bio-industries innovantes. Les glucides constituent la classe de biomolécules la plus abondante sur Terre, puisqu'ils sont le principal constituant de nombreuses espèces vivantes, des plantes aux champignons, en passant par les algues, les crustacés, les insectes et les animaux d'ordre supérieur. Cependant, il reste encore beaucoup à découvrir et on les appelle parfois la "matière noire" des biomolécules, par rapport aux lipides, aux protéines ou aux acides nucléiques.
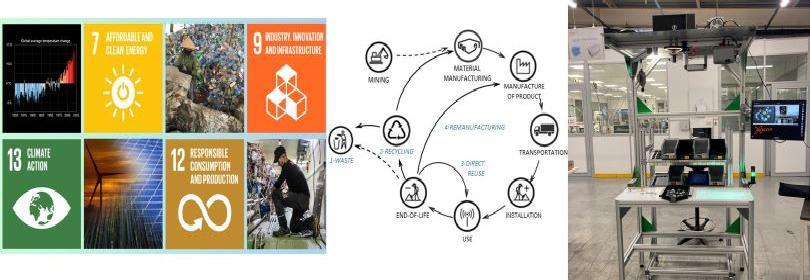
G-SCOP est impliqué dans le work package qui se penche sur l'étude du potentiel des carbohydrates, depuis la paillasse des laboratoires de recherche fondamentale jusqu'à la chaîne de production des industries, tout en tenant compte des principales considérations sociétales et environnementales, telles que le cycle de vie. En particulier, le G-SCOP, en collaboration avec des scientifiques de différents groupes du réseau, se concentrera sur le potentiel de mise à l'échelle des processus émergents liés aux glycanes. Il s'agira de considérer l'ensemble de leur cycle de vie, y compris leur utilisation finale et les systèmes industriels nécessaires à l'industrialisation de produits à base de polysaccharides ayant des impacts environnementaux et sociaux compatibles avec les objectifs de soutenabilité (par exemple, les limites planétaires).
After 4 years of cross-cutting project, the Glyco@Alps2 programme will continue to explore the diversity and structural complexity of sugars, including those found in Alpine biodiversity, and focus on their exploitation for biopharmaceuticals, medical diagnostics, personalised medicine, materials and innovative bio-industries. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of biomolecules on Earth, being the main constituent of many living species, from plants to fungi, algae, crustaceans, insects and higher order animals. However, much remains to be discovered and they are sometimes referred to as the 'dark matter' of biomolecules, as opposed to lipids, proteins or nucleic acids.
G-SCOP is involved in the work package that looks at the potential of carbohydrates, from the bench of basic research laboratories to the production line of industries, while taking into account key societal and environmental considerations, such as life cycle. In particular, the G-SCOP, in collaboration with scientists from different network groups, will focus on the potential for scaling up emerging glycan processes. This will involve considering their entire life cycle, including their end-use and the industrial systems needed to industrialise polysaccharide-based products with environmental and social impacts compatible with sustainability objectives (e.g. planetary limits).
Informations sur Glyco@Alps2
- Porteur du projet : Romain Vivès (IBS)
- Responsable scientifique G-SCOP : Damien EVRARD
- Durée: 2022 - 2026
- Organisme de financement : IDEX UGA
Responsable et contact
 +33 (0)
+33 (0)4 76 82 70 24 Bureau: C 312 |